Software trends in supply chain & inventory management

Software trends in supply chain & inventory management
Supply chain and inventory management have seen radical changes with the recent integration of AI technologies. Companies from numerous industries are increasingly resorting to innovative software solutions to enhance their supply chain capabilities and operations; resulting in a major increase in efficiency. According to Statista, 40% of supply chain industries have already integrated emerging technologies, and the number is expected to surge in the future. This shows how software technologies are transforming production and supply chains for numerous businesses.
Today's warehousing and logistics providers use technology to control warehousing and logistics processes in order to achieve economies of scale and competitiveness, as well as to create leaps and bounds of innovation to accommodate expanding demand. Furthermore, many warehouse service providers have invested in technology to enable online order management throughout the entire process, from linking data to receiving orders from marketplaces, preparing products, picking and packing products, and delivering to end customers. Time constraints People issue errors and issues with the product are also present, read more.
With the latest integration of supply chain technologies, this article will explore digital transformation, as well as how it is driving change in the industry and the way businesses deliver value to customers.
![]()
Inventory Tracking and Management:
-
Real-time inventory visibility:
This offers up-to-date and real-time information on each SKU for every inventory storage location. This allows companies to maximize efficiency and resource allocation.
-
Stock level monitoring and alerts:
Indicative of its name, this software method allows a notification to be sent electronically once a preset level (reorder level) is reached. This can be used for specific products selected within the software.
-
Batch/lot tracking:
Commonly used in batch production, batch/lot tracking provides real-time information such as location, date of manufacture, expiration date, and much more. Batches are groups of products produced in one production process, and tracking this information allows for better management.
-
SKU and barcode management:
Similar to barcodes, Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) are used to identify information about specific products corresponding to a unique alphanumeric code. Nowadays, SKU management is widely used in e-commerce websites to ensure high accuracy in inventory levels, warehouse organization, and order tracking.
-
Inventory optimization and demand forecasting:
Demand forecasting can be used to predict future demands and allows businesses to optimize inventory with the help of inventory management software by storing current data. This reduces excessive inventory, ultimately reducing inventory costs for firms when utilized correctly.

Order Management:
-
Order processing and fulfillment:
Digitally processing orders and fulfilling them ensures customers receive their products promptly and quickly since everything can be easily tracked and managed. Successfully accomplishing this can increase customer satisfaction, avoid late deliveries, and enhance the brand's reputation.
-
Automated order routing and allocation:
Integrating software and hardware can allow firms to create an automated conveyor belt system that automatically sorts and allocates items needed to be shipped quickly and efficiently. This is especially important for bigger companies as inventory and items are increasingly becoming harder to track due to the larger quantities.
-
Order tracking and status updates:
Order tracking ensures customers have a holistic view of the delivery location and estimated time of delivery, which can enhance their experience throughout the process. They can also be easily informed if there is a delay with their orders.
-
Returns and reverse logistics management:
This process involves managing items being returned from customers back to the provider/seller due to various reasons such as delivery failure or products no longer functioning. This process is crucial for sellers to obtain feedback and allow products to be recycled and correctly returned to reduce inventory loss. These returns are estimated to be worth nearly a trillion dollars annually.

Warehouse Management:
-
Warehouse layout and bin management:
Having a good bin location reduces potential errors and saves time while picking items within the warehouse. It also reduces the time taken to access specific items, which increases overall efficiency. Businesses with warehouses must consider the levels, area, row, and bin location to optimize inventory management.
-
Pick, pack, and ship processes:
-
Pick: Select products from the storage to be shipped to customers, and there may be specific areas designated for collecting and picking the products.
-
Pack: Products are packed either using specialized machines or manual work and prepared for shipment. Labels are also attached to track information in the software.
-
Ship: The packed orders are then sent to delivery companies for shipment to the buyer's destination. This process is crucial to ensure that products aren't damaged during transit.
-
Inventory replenishment and put-away:
Put-aways involve receiving goods and storing them in a warehouse. As low inventory levels are identified, inventory is replenished to ensure there are enough products to meet consumer needs. Making the inventory replenishment process as efficient as possible allows businesses to prevent potential reductions in sales.
-
Cross-docking and order consolidation:
Order consolidation is the process of grouping smaller orders together to reduce transportation costs. Similarly, cross-docking is when products are shipped out on the same day they are received. Both of these processes aim to reduce costs for businesses and improve warehouse utilization and efficiency.
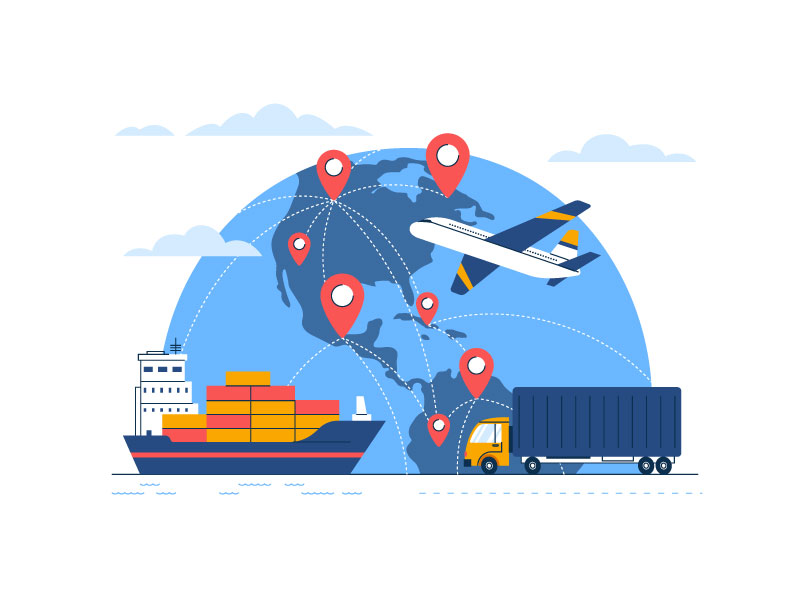
Transportation Management:
-
Route planning and optimization:
Route planning and optimization help delivery vehicles take the least possible distance to deliver multiple orders. This is accomplished by using highly technical algorithms to calculate the best possible route, which takes into account customer location, product requirements, and road traffic. This allows for a smoother and better experience for both customers and drivers.
-
Carrier selection and rate management:
Using software to track and monitor the performance of individual carriers allows businesses to reduce potential disruptions to supply chain operations. Additionally, it also enables businesses to become more mobile and adapt to new challenges.
-
Shipment tracking and visibility:
Integrating GPS into current software offers both buyers and sellers the ability to track the location of carriers and enhance their supply chain visibility. Such technologies could potentially be combined with machine learning software to consider the weather and external conditions that could influence performance and productivity.
-
Freight audit and payment:
Freight audit and payment is the process of examining all expenses and performance data to calculate and enhance visibility on transportation costs and profitability. This not only provides business insights to minimize unnecessary labor costs but also helps easily detect and respond to errors.

Analytics and Reporting:
-
Customizable dashboards and reports:
Dashboards provide a visual and graphical representation of compiled reports from multiple data sources within the supply chain. This allows the entire organization to view and understand key data and identify areas for improvement.
-
Key performance indicators (KPIs) tracking:
KPIs are essential data that businesses use on a day-to-day basis, as they help businesses achieve their objectives and improve financial and operational performance. Tracking KPIs provides up-to-date information and helps businesses make more accurate decisions in a constantly changing industry.
-
Data visualization and trend analysis:
Data visualization and trend analysis are vital as they extract key insights from numerous fields of complex data and identify emerging trends. With the aid of big data analytics, organizations can now analyze larger and even more complex datasets to maximize their performance.
-
Supply chain analytics for insights and decision-making:
Supply chain analytics involves the complex analysis of data throughout the entire supply chain to fully understand operations and assist in planning. It can also enable companies to reduce costs and mitigate risks within the supply chain.
These software solutions for supply chain and inventory management now offer essential features, catering to both businesses and individuals. When incorporated, software can not only maximize efficiency but also significantly streamline operations to further enhance an organization's supply chain and inventory control. Harnessing such technologies is vital for businesses to keep up with the current trend of digital transformation.
Source:
https://www.ibm.com/watson/supply-chain/resources/real-time-inventory-visibility/
https://www.shipwire.com/support/inventory-alert-learn-more/
https://tulip.co/blog/lot-tracking-batch-tracking-for-manufacturers/
https://zayls.com/knowledgebase/faqs/the-difference-between-sku-and-barcode/
https://www.shipbob.com/blog/sku-management/
https://www.inboundlogistics.com/articles/order-fulfillment/
https://www.cnbc.com/2019/01/10/growing-online-sales-means-more-returns-and-trash-for-landfills.html
https://www.magestore.com/bin-location/
https://flow.space/blog/what-is-pick-pack-and-ship/
https://www.eurosender.com/blog/en/pick-pack-ship/
https://www.mountainleverage.com/put-away-and-inventory-replenishment-what-can-voice-do-for-you/
https://blog.coleintl.com/blog/consolidation-and-cross-docking
https://www.traxtech.com/blog/what-is-carrier-management
https://www.redwoodlogistics.com/what-is-freight-audit-and-payment-definition-importance/
https://www.datapad.io/blog/how-to-track-kpis
https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-some-current-trends-challenges-data
https://www.bradyid.com/intelligent-manufacturing/rfid-vs-barcode


Subscribe to follow product news, latest in technology, solutions, and updates
Other articles for you



Let’s build digital products that are simply awesome !
We will get back to you within 24 hours!Go to contact us Please tell us your ideas.
Please tell us your ideas.