Combining Multiple Sitemaps with an Index File (For Large-Scale Sites)

For large websites with tens of thousands or more pages, managing SEO and search engine indexing presents challenges. A key task is handling the sitemap structure to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl and index your content. A single sitemap often becomes unwieldy due to size limits, so the solution for large sites is to use multiple sitemaps combined into one master file, known as a sitemap index file.
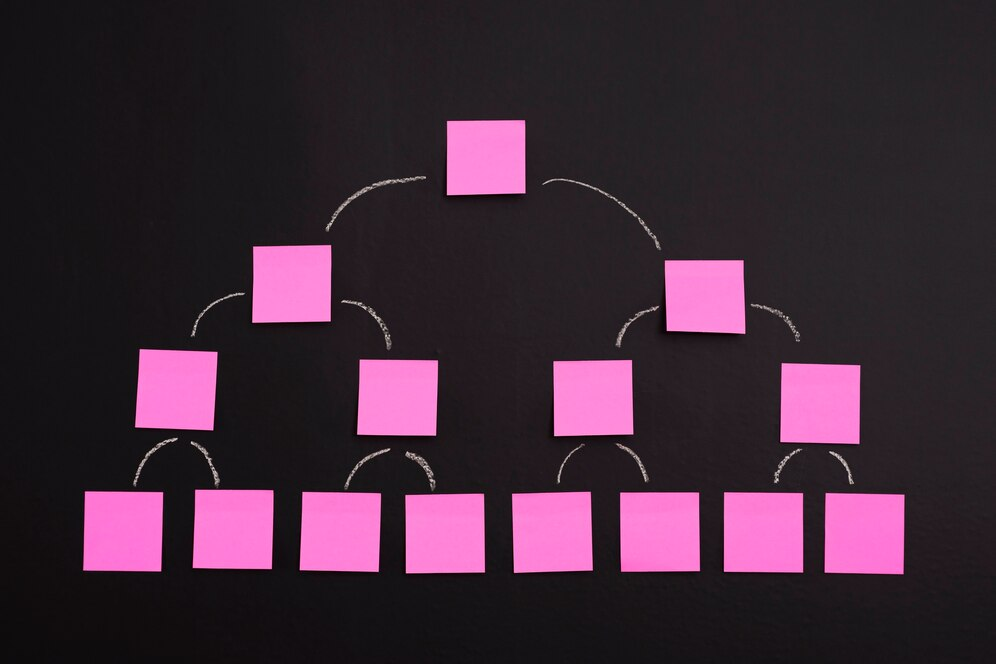
What is a Sitemap Index File?
A sitemap index file is a file that lists multiple individual sitemaps instead of directly listing URLs. It functions as a directory or table of contents, helping search engines like Google find and crawl all the individual sitemaps associated with your website. Each referenced sitemap may be organized by content type, section, or other criteria, making it easier to manage large-scale sites.
Why Use Multiple Sitemaps and a Sitemap Index File?
-
Overcoming Size Limits: Google allows each sitemap to have a maximum of 50,000 URLs and 50MB in uncompressed size. By splitting your content into multiple sitemaps, you stay within these limits.
-
Enhanced Crawl Efficiency: Organizing sitemaps by content type or category allows search engines to crawl and prioritize your pages more intelligently, improving indexing speed and accuracy.
-
Simplified Management: With multiple smaller sitemaps, it’s easier to update or fix issues without affecting the entire site. For example, if one sitemap needs an update, it doesn’t disrupt other sections.
-
Improved Diagnostics: Smaller sitemaps make it easier to detect and troubleshoot crawl errors, as issues can be traced directly to the specific sitemap or section.
Organizing Your Sitemaps
Effective sitemap organization is key to managing a large website. Here are several strategies:
-
By Content Type: Group URLs by content types like blog posts, product pages, videos, or images. This makes it easier for search engines to prioritize relevant content.
-
By Website Sections: If your website is organized into clear sections or categories, create separate sitemaps for each. For example, an e-commerce site may have sitemaps for product categories, while a blog may have sitemaps for posts, comments, and images.
-
By Date/Timeframe: If your website is content-heavy (like news or blogs), create sitemaps based on publication date, such as monthly or yearly sitemaps.
-
By Language or Region: For multilingual or international sites, consider creating separate sitemaps for different languages or regions to improve global SEO performance.
Best Practices for Using Multiple Sitemaps and a Sitemap Index File
-
Use Clear and Consistent Naming: Name your sitemap files logically, like
products-sitemap.xmlorblog-sitemap.xml, for easy identification and management. -
Keep Sitemaps Updated: Regularly update your sitemaps to reflect changes in your content. Automating this process through SEO tools or CMS is ideal.
-
Verify Sitemaps Individually: Google Search Console allows you to submit both the individual sitemaps and the sitemap index. Verifying them separately provides better insights into indexing status.
-
Limit URLs per Sitemap: Although Google allows 50,000 URLs, aiming for smaller sitemaps (around 10,000–20,000 URLs) generally improves processing speed and troubleshooting.
-
Include Your Sitemap Index in Robots.txt: To ensure search engines easily find your sitemap index file, include it in your site's
robots.txtfile. -
Monitor Sitemap Performance: Use Google Search Console to track the status of your sitemaps and fix any errors quickly.
-
Balance Sitemap Granularity: Avoid creating too many small sitemaps or one massive sitemap. Aim for a manageable structure that maintains efficiency and simplicity.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How Many Sitemaps Can Be in an Index File?
Google allows up to 50,000 sitemaps in one sitemap index. However, most large sites will manage with dozens or hundreds of sitemaps. -
Should I Submit All Sitemaps to Google Search Console?
Submitting the sitemap index file is usually sufficient. However, submitting each individual sitemap provides more detailed tracking and diagnostics. -
How Often Should I Update the Sitemap Index?
Update the index when adding or removing individual sitemaps. Automating this process is recommended.
Conclusion
Using multiple sitemaps combined through a sitemap index file is an effective strategy for managing large websites. This structure allows search engines to crawl and index content efficiently, improving your site's visibility and SEO performance. By organizing your sitemaps logically, keeping them updated, and monitoring their performance, you can ensure optimal indexing and easier management, leading to better search engine results for your website.


Subscribe to follow product news, latest in technology, solutions, and updates
Other articles for you



Let’s build digital products that are simply awesome !
We will get back to you within 24 hours!Go to contact us Please tell us your ideas.
Please tell us your ideas.