Canonical Tags: Avoiding Duplicate Content Penalties
Share

Duplicate content is one of the most misunderstood and underappreciated challenges in search engine optimization. While having similar content across multiple pages may seem harmless, it can confuse search engines, split ranking power, and dilute your SEO effectiveness.
The solution? Canonical tags.
Used correctly, canonical tags can help search engines understand which version of a page you want indexed, protecting your site from duplicate content issues and consolidating SEO signals for better visibility.
In this article, we’ll break down how canonical tags work, why they matter, and how one fashion retailer boosted their organic traffic by 18% just by using them to streamline duplicate product pages.
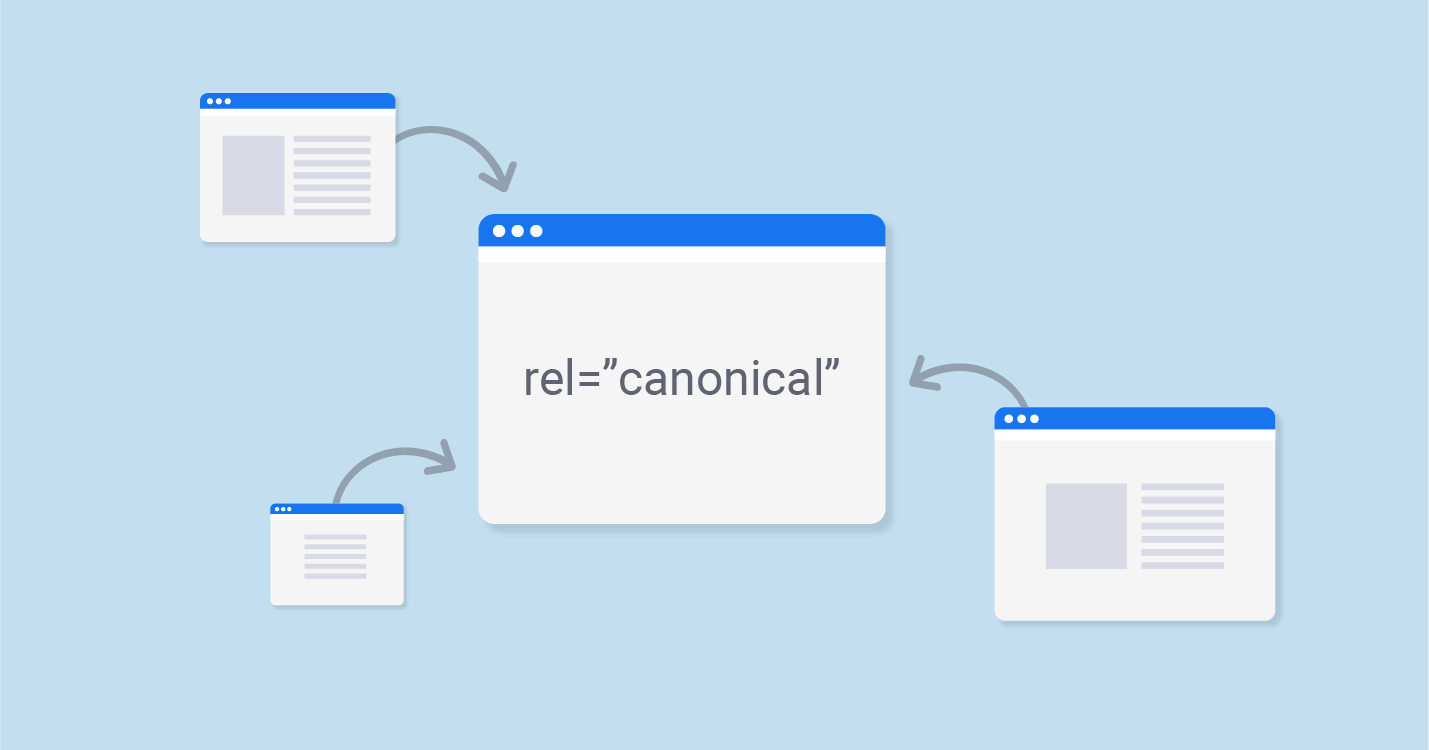
What Is a Canonical Tag?
A canonical tag is an HTML element placed in the head of a web page. It tells search engines which version of a page should be considered the "canonical" or original source when multiple versions with similar content exist.
For example, if your site has the same product accessible through different URLs—due to filters, categories, or tracking parameters—you can use a canonical tag to point them all back to the preferred version.
Search engines will then focus their indexing and ranking efforts on that primary URL.
Why Duplicate Content Happens
Duplicate content can occur for a number of reasons, especially on large or dynamic websites. Common causes include:
-
URL parameters for sorting and filtering (e.g., /product?color=red vs /product?color=blue)
-
Printer-friendly versions of pages
-
HTTP vs HTTPS versions
-
www vs non-www URLs
-
Content syndication or reposting
-
Pagination of long articles or product listings
While Google does a decent job of detecting and handling duplicate content, relying on algorithms alone is risky. Canonical tags give you control over how content is interpreted and indexed.
Why Canonical Tags Matter for SEO
1. Consolidate Ranking Signals
When several pages share similar content, link equity and ranking power may be split between them. A canonical tag consolidates these signals, making your chosen page stronger in search rankings.
2. Improve Crawl Efficiency
Search engines have a limited crawl budget. By signaling your preferred pages, you help bots spend more time on unique, high-value content instead of crawling duplicates.
3. Prevent Unwanted Indexation
Without canonicalization, search engines might index non-preferred pages—like those with URL parameters or session IDs—resulting in cluttered search results and lost traffic opportunities.
4. Avoid Content Dilution and Penalties
While Google doesn’t typically penalize sites for unintentional duplicate content, too many similar pages can lead to poor performance. Canonical tags prevent this by reinforcing which content matters most.
Real-World Case: Fashion Retailer Streamlines SEO with Canonical Tags
A mid-sized fashion retailer had a large product catalog, with each item accessible through multiple URLs based on size, color, and category filters.
For instance, the same pair of jeans could be viewed through:
-
/jeans/women/blue
-
/products/blue-jeans?size=m
-
/sale-items/blue-jeans
Although each URL served a business purpose, they created an SEO mess. Google indexed multiple versions of the same page, splitting visibility and making it difficult to rank consistently.
What They Did:
-
Conducted a full crawl using SEO tools to identify all duplicate product pages
-
Chose a single URL as the canonical version for each product
-
Added canonical tags to all alternate URLs, pointing them to the master version
-
Updated their sitemap to include only canonical URLs
-
Monitored changes in Google Search Console and third-party analytics
The Results:
-
Google began consolidating link equity across duplicate pages
-
Search visibility improved for several high-value product categories
-
Organic traffic increased by 18% within three months
-
The SEO team was able to focus efforts on fewer, higher-impact pages
This simple fix helped the retailer clean up their search presence without deleting any content or making drastic changes to their URL structure.
How to Use Canonical Tags Effectively
1. Choose the Right Canonical URL
Pick the most representative, SEO-friendly version of a page. This is usually:
-
The cleanest URL (without tracking codes or filters)
-
The version with the most backlinks
-
The one linked to most internally
2. Add the Canonical Tag
Place the canonical tag in the <head> section of all versions of the page, pointing to the chosen URL. Even the canonical version should reference itself.
Example (not shown as code, per request):
-
For /product/blue-jeans, all alternate versions should indicate /product/blue-jeans as canonical.
3. Use Absolute URLs
Canonical tags should always use full URLs, not relative paths. This ensures consistency and avoids interpretation errors.
4. Be Consistent Across Your Site
Canonical tags should match your internal linking structure, sitemap entries, and preferred domain configuration (e.g., HTTPS vs HTTP).
5. Monitor and Test
Use tools like:
-
Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool
-
Screaming Frog or Sitebulb for site-wide audits
-
Analytics platforms to compare traffic before and after changes
What Canonical Tags Don’t Do
It’s important to understand the limitations of canonical tags:
-
They are suggestions, not commands. Search engines usually respect them, but not always.
-
They do not redirect users. For that, use a 301 redirect.
-
They don’t prevent bots from crawling the page—they only influence which version appears in search results.
Alternatives and Complements to Canonicalization
-
301 Redirects: Use these when duplicate pages should not exist at all
-
Noindex Meta Tag: Use when a page should not be indexed under any circumstances
-
Hreflang Tags: Use to handle regional content variants across different languages or countries
Conclusion
Duplicate content doesn’t have to be a penalty—it just has to be managed. With the strategic use of canonical tags, you can clarify your site’s structure, consolidate ranking power, and guide search engines toward your most valuable content.
For businesses with dynamic websites, product variants, or a growing blog archive, canonical tags are a powerful and low-effort way to sharpen your SEO strategy.
Understanding and applying canonical tags correctly could be the difference between a cluttered search presence and a streamlined, high-performing SEO profile.
Would you like a simple visual diagram or checklist summarizing when and how to use canonical tags for your marketing team or blog?

Share

Keep me postedto follow product news, latest in technology, solutions, and updates
Related articles
Explore all


